“The magic of America is that we’re a free and open society with a mixed population. Part of our security is our freedom.” – Madeleine Albright
Live the American Dream and move to the United States., a cultural melting pot with a booming economy, a wealth of opportunities, and one of the highest standards of living anywhere on the globe.
What makes it special?
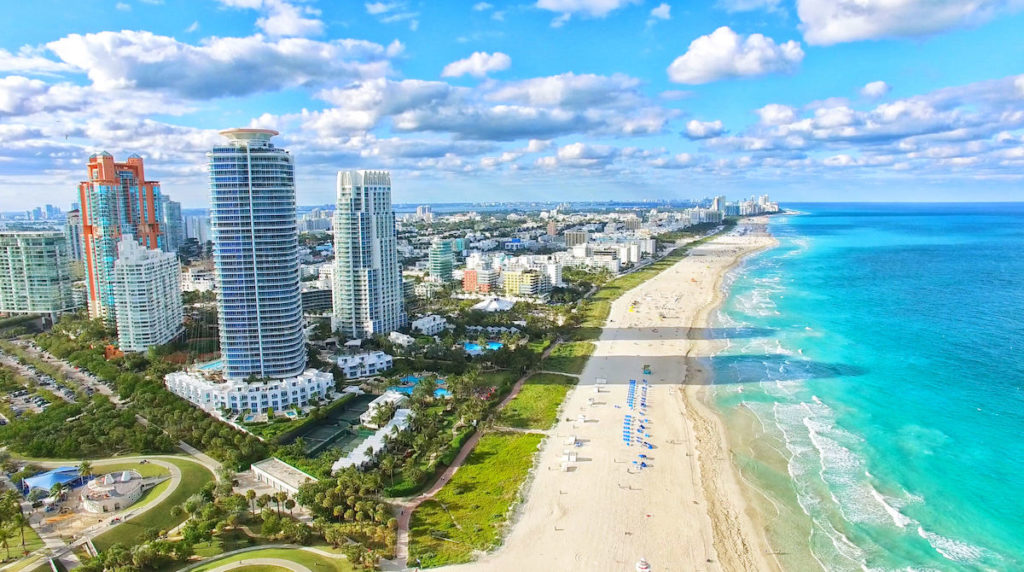
The great American experience is about so many things – skyscrapers and beaches, snow-covered peaks and redwood forests, vast desserts and big open skies.
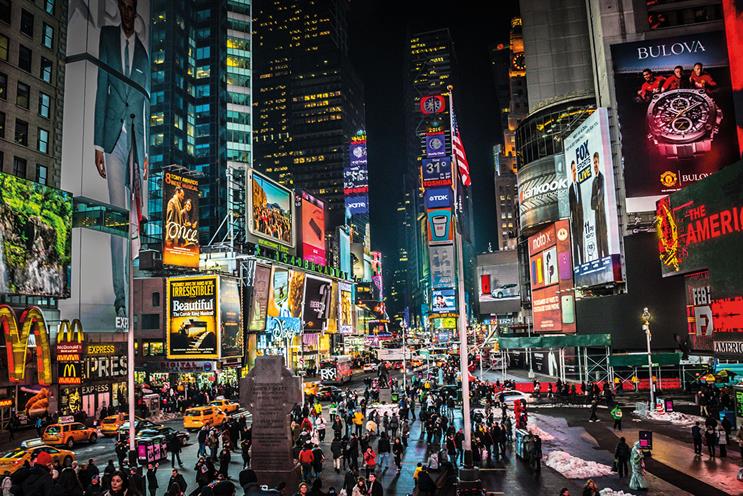
America is the birthplace of LA, Las Vegas, Chicago, Miami, Boston and New York City – each a brimming metropolis whose name alone speaks of a million different notions of culture, cuisine and entertainment.
This is a country of road trips and great open skies, where 4 million miles of highways lead past red-rock deserts, below towering mountain peaks and through fertile wheat fields that roll off toward the horizon. The sun-bleached hillsides of the Great Plains, the lush rainforests of the Pacific Northwest, the sultry swamplands of the South and the scenic country lanes of New England are a few fine starting points for the great American road trip.
Key Facts:
Climate – mostly temperate, but tropical in Hawaii and Florida, arctic in Alaska, semiarid in the great plains west of the Mississippi River, and arid in the Great Basin of the southwest; low winter temperatures in the northwest are ameliorated occasionally in January and February by warm chinook winds from the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains
Population (2020) – 328,239,523
GDP (Per Capita) (2020) – $67,426
Official language – English (national language)
Major religions – Christianity (73%), Judaism (2.1%), Islam (0.8%)
Ethnic Groups – White (73.1%), Black (13.4%), Multiracial (6.1%)
Government – constitutional federal republic
Currency – United States Dollar (USD)
Taxes – All US citizens and residents, including resident aliens and citizens who reside outside the US, pay federal tax on their worldwide income, with credits for foreign income taxes (subject to certain limitations). Individuals generally must include gross income from whatever source derived in their taxable income, including compensation for services (all forms of remuneration and allowances and the value of other perquisites that are not specifically exempted), dividends, interest, royalties, rents, fees and commissions, gains from dealings in property, and income from a partnership, limited liability company, S corporation, estate, or trust. Rates are progressive up to 37%. For 2019, the threshold for the 37% bracket is USD 510,300 for single taxpayers and USD 612,350 for married taxpayers filing jointly. In addition to the regular income tax, individuals may be subject to the alternative minimum tax (AMT), which is triggered where an individual’s tentative AMT liability exceeds that individual’s regular income tax liability. The AMT is imposed at a rate of 26% on the taxable excess (AMT income minus an “exemption amount”) up to specified levels, and at a rate of 28% on the taxable excess above these levels. The exemption amounts for the individual AMT for 2019 are USD 111,700 for married taxpayers filing jointly and USD 71,700 for unmarried taxpayers and will be automatically indexed for inflation thereafter. The excess of net long-term capital gains (generally, gains from investments held for more than one year, although the holding period requirement is expanded to three years for gains on qualified carried interests) over net short-term capital losses (net capital gains) generally is taxed at a maximum rate of 20%. The net capital gains rate also is applicable to qualified dividends received from domestic corporations generally and from certain foreign corporations.
Residency by Investment:
Permanent Residents (often called green card holders) are authorized to live and work on a permanent basis in the U.S. Whereas most nonimmigrants must document their intent to depart the U.S. after a period in the U.S., green card holders should have the intent to remain in the U.S.There are several ways to obtain permanent residency in the U.S, including:
- A petition from an employer
- The employment-based green card application system allows for five preference categories, commonly abbreviated as EB-1, EB-2, etc. Each preference category may have several sub-categories.
- Marriage to a U.S. citizen
- Sponsorship by a close relative who is a U.S. citizen or legal permanent resident
- The U.S. Department of State diversity lottery program.
Citizenship by Investment:
Investment Options – The USA EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program comprises two investment options:
Option 1 – Creation of a New U.S. Enterprise:
To be eligible for this investment option, applicants must meet the following criteria:
Make an investment of US$1.8 million in a new commercial enterprise or US$900,000 if that enterprise is in a targeted commercial area, including rural areas or areas with unemployment of at least 150 percent that of the national average.
Create full-time employment for at least 10 qualified U.S. workers who must be direct employees of the commercial enterprise.
Actively manage the day-to-day activities and/or policy formulation of the enterprise.
Option 2 – Investment in a Regional Center:
Regional centres are investment opportunities that have been pre-approved by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services. To be eligible for this investment option, applicants must meet the following criteria:
- Make an investment of US$900,000.
- Create full-time employment for at least 10 qualified U.S. workers, where indirect employment is permitted.
- Active management of the enterprise is not required.
Why it makes sense?
- There are no language skills required.
- There is no minimum education required.
- There is no business or managerial experience required.
- Investment capital can come from a gift, inheritance, business ownership or any other lawful activity.
- There is no obligation to live in the area of investment.
- The opportunity to live, work and study anywhere in the U.S. and benefit from lower tuition fees.
- Inclusion of dependent children under the age of 21.








